Don't forget to hit the ⭐ if you like this repo.
Module 1: Introduction to Software Engineering
Group Explorer
- KOH LI HUI A22EC0059
- LOW JIE SHENG A22EC0075
- CHEN PYNG HAW A22EC0042
- The Importance of Software Engineering
- Software Engineering Costs
- Software Engineering in Software Development
- Software Engineering Definition
- Software Engineering as a Layered Technology
- Software Products and Product Specification
- Software Engineering Diversity:Types of Software
- Inherent Difficulties
- Software Complexity
- Software Changeability
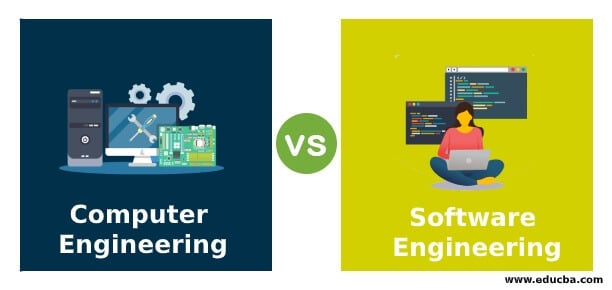
- Computer Science vs.Software Engineering
- Software Engineering vs.Software Programming
- Quality Focus
- Quality Focus: Example of Software Quality
- Quality Priority
- Software Standard and Document
- To understand the importance of software engineering in software development
- To understand the definition of software engineering
- To know the difference between Software Engineering and Computer Science, Software Engineering and Software Programming
- To understand the importance of software quality and documentation standard
- Software Engineering | Introduction to Software Engineering
- Document standards by IEEE
- 830-1998 - IEEE Recommended Practice for Software Requirements Specifications
- 1016-2009 - IEEE Standard for Information Technology--Systems Design--Software Design Descriptions
- 829 - IEEE Standard for Test Documentation Overview-Test Plan Outline
- 829-2008 - IEEE Standard for Software and System Test Documentation
- IEEE Standards
Software engineering is an essential field of study that deals with the design, development, and maintenance of software applications. It plays a vital role in the development and success of modern technology. The importance of software engineering can be seen in many areas of modern society, including business, healthcare, education, and entertainment.
Why software engineering is important?
- Reduces Complexity
- Help to simplify complex problems and solve those issues one by one.
- Handling Big Projects
- Big projects need lots of patience, planning, and management, which you never get from any company. The company will invest its resources; therefore, it should be completed within the deadline. It is only possible if the company uses software engineering to deal with big projects without problems.
- Minimize Software Costs
- Software engineers are paid highly as Software needs a lot of hard work and workforce development. These are developed with the help of a large number of codes. But programmers in software engineering project all things and reduce the things which are not needed. As a result of the production of Software, costs become less and more affordable for Software that does not use this method.
- Decrease Time
- If follow the prescribed software engineering methods, it will save the precious time by decreasing it.
- Enables the creation of complex software systems that can automate tasks and increase efficiency
- This can be seen in industries such as finance and manufacturing, where software is used to automate processes and reduce the likelihood of human error.
- Ensure the quality and reliability of software systems
- The software will be reliable if software engineering, testing, and maintenance are given.
- By applying engineering principles and rigorous testing methodologies, software engineers can identify and correct potential issues before they impact end-users.
- Collaboration
- Software engineering fosters collaboration among developers, designers, and stakeholders, which helps ensure that software systems are developed with the end user in mind. This collaboration also helps improve communication, reduce errors, and ensure that software meets the needs of all stakeholders.
- Ensuring security and privacy
- Software engineers can design systems that are resistant to cyberattacks and ensure that user data is protected.
Overall, software engineering is a vital discipline that plays an important role in many areas of modern society. Its benefits include improved quality and reliability of software systems, increased efficiency and automation, improved security and privacy, and the ability to drive innovation and advance technology.
Software engineering costs refer to the expenses incurred during the development, maintenance, and deployment of software.Software engineering costs can be categorized into several types, including:
-
Development costs: These include the costs associated with creating the software, such as salaries of the development team, tools, hardware, and software licenses.
-
Maintenance costs: These include the costs of fixing bugs, adding new features, and ensuring that the software remains up to date with changes in the operating system or other dependencies.
-
Testing costs: These include the costs of testing the software to ensure that it is functioning as intended and is free from bugs or errors.
-
Deployment costs: These include the costs associated with deploying the software to the production environment, such as server costs, deployment tools, and user training.
-
Support costs: These include the costs of providing customer support and responding to user inquiries or issues.
-
Upgrading costs: These include the costs of upgrading the software to a newer version or technology, such as migrating from an on-premise system to a cloud-based one.
Software engineering costs can be significant, and it's essential to estimate and manage them effectively to ensure that the software is developed within the allocated budget and timeframe. By carefully considering all the costs associated with software engineering, development teams can make informed decisions about resource allocation, and ensure that the software is built efficiently and effectively.
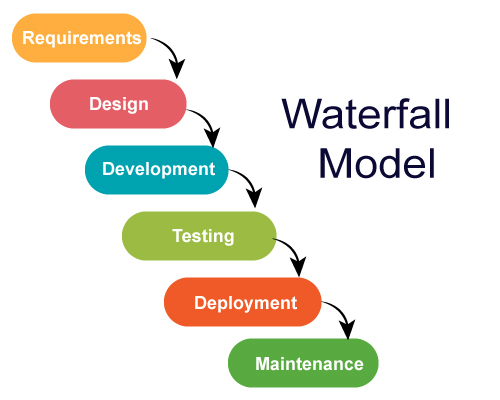
In software development, software engineers use software engineering principles to create high-quality software systems that meet the requirements of end-users. The software development process includes requirements analysis, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance.
Software engineering is a field in which technical principles and practices are applied to the design, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance of software systems. It is a systematic approach to software development that uses formal methods, processes, and tools to ensure that software systems are reliable, efficient, and maintainable.
Software engineering also involves the use of quality assurance processes to ensure that the software is developed to a high standard. These processes may include testing, code reviews, and documentation. Software engineering also includes project management and collaboration, as software development is usually a team effort involving multiple developers and stakeholders.
Overall, software engineering provides a structured and disciplined approach to software development that helps ensure that software systems are developed to high standards and meet end-user requirements.
Software engineering is a discipline that involves the application of engineering principles, methods, and techniques to the design, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance of software systems. It is a structured and systematic approach to software development that aims to ensure the reliability, efficiency, and maintainability of software systems.
Software engineering involves a range of activities, including requirements gathering, design, coding, testing, and documentation. It also involves the use of various tools and techniques to manage the software development process, including project management tools, version control systems, and automated testing tools.
The goal of software engineering is to create high-quality software systems that meet the needs of end-users, are reliable and efficient, and can be maintained and updated easily. Software engineering is a collaborative discipline that involves software engineers, project managers, quality assurance specialists, and other stakeholders in the software development process.
Overall, software engineering is a vital discipline that underpins the development of the software systems that are used in many areas of modern life, from business and finance to healthcare and entertainment.
-
Quality Focus: Quality orientation is an important aspect of software engineering that focuses on the quality of the software system throughout the development process. This means that software engineers must focus on continuously improving the development process and ensuring that the final product meets the required quality standards. A quality orientation requires the use of various quality assurance processes and techniques, such as code reviews, testing and documentation.
-
Process: Process is the foundation of software engineering and provides a framework for the streamlined and timely development of computer software. A well-defined and structured process enables software engineers to manage the complexity of software development and ensure that the software system is developed on time and within budget. The process includes various phases, such as requirements analysis, design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance.
-
Methods: Methods provide technical guidelines and guidance for building software. They encompass various tasks, including requirements analysis, design, program development, testing, and support. Methods also include modeling activities, such as creating diagrams and other representations of the software system. By following well-defined methods, software engineers can ensure that the software system is developed in a structured and systematic manner.
-
Tools: Tools provide automatic or semi-automatic support for the software development process and methods. They help automate repetitive tasks, provide support for testing and debugging, and improve collaboration between software development teams. Tools include integrated development environments (IDEs), version control systems, testing frameworks and other utilities for software development.
In summary, quality focus, process, methods, and tools are essential components of software engineering that work together to ensure the development of high-quality software systems that meet the needs of end-users.
Software products are software systems or applications that are developed to meet the specific needs of end-users. A software product can be anything from a simple mobile app to a complex enterprise-level software system.
Product specification is a critical aspect of software product development that involves defining the functional and non-functional requirements of the software product. Product specification provides a detailed description of the software product, including its features, functionality, performance, and other relevant characteristics.
-
Generic products: software systems or applications that are tailored to meet the needs of a broad range of users or organizations. These products are usually preconfigured and sold as off-the-shelf solutions that are easy to implement and configure. Generic products are often less expensive than custom products because they are developed for a broader audience and can be sold to multiple customers.
-
Custom products: software systems or applications that are tailored to the specific needs of a particular customer or business. These products are usually developed from scratch or are based on existing software products that are customized to meet the customer's specific requirements. Customized products are often more expensive than generic products because they require a higher degree of customization and development effort.
The choice between generic and custom products depends on several factors, including the customer's specific requirements, the degree of customization required, and the available budget. Generic products are often a good choice for companies that need a software solution that can be implemented quickly and requires minimal customization. Custom products are often a better choice for companies that have specific requirements that cannot be met by a generic product and are willing to invest the time and money required to develop a custom solution.
Product specification plays a crucial role in software product development because it helps to ensure that the software product meets the needs of end-users and is delivered on time and within budget. A well-defined product specification helps to ensure that the software product is developed in a structured and systematic way, and that all stakeholders are clear on the product's requirements and goals.
Software diversity is a research field about the comprehension and engineering of diversity in the context of software.To build a software at first we fixed our requirements and according to our requirements we have to choose perfect software design and implementation techniques. For different software we have to select different kinds of techniques.
-
System software: This type of software is designed to provide a platform for other software to run on. It includes operating systems, device drivers, utilities, and programming language translators. Examples of system software include Windows, Linux, device drivers, and compilers.
-
Real-time software: Real-time software is a type of software that is designed to respond to events or input within a specific timeframe. In real-time software, the output or response to an input is required within a specified time interval to meet the system's requirements. Real-time software is commonly used in systems that require high reliability and safety, such as aerospace, defense, and medical equipment.
-
Business Software: Business software is any software or set of computer programs used by business users to perform various business functions. These business applications are used to increase productivity, measure productivity, providing real-time insights, streamlining processes and perform other business functions accurately.
-
Embedded software: Embedded software is a type of software that is designed to be embedded into a hardware device or system to control its functionality. It is used in a wide range of applications, including consumer electronics, automotive systems, medical devices, and industrial control systems.It is often programmed in low-level languages, such as C and Assembly, to optimize performance and reduce memory usage.
-
System for modeling and simulation: A system for modeling and simulation is a software tool or platform that allows users to create, run, and analyze models of complex systems in various domains, such as engineering, physics, economics, and biology. These systems use mathematical and computational models to simulate the behavior of real-world systems, and they can be used to explore different scenarios, make predictions, and test hypotheses.
-
Stand alone application: A stand-alone application is a software application that can run on a computer system without requiring any additional software or resources. These types of applications are often referred to as "native applications" because they are designed specifically for a particular operating system or platform, such as Windows, Mac OS, or Linux. Examples of stand-alone applications include Word processing, spreadsheets, computer graphics, multimedia, entertainment, personal and business financial applications.
-
Interactive transaction-based software: Interactive transaction-based software is a type of software application that allows users to interact with a computer system to complete transactions or tasks. These types of software are designed to facilitate interactions between users and computer systems, allowing users to perform tasks such as making a purchase, booking a reservation, or completing a financial transaction. Examples of interactive transaction-based software include online banking systems, e-commerce websites, and reservation booking systems.
-
Artificial intelligence software: Artificial intelligence (AI) software refers to software applications that use machine learning algorithms and other AI techniques to simulate human intelligence and perform tasks that typically require human intervention. These software applications can be used for a wide range of purposes, from automating business processes to assisting with medical diagnosis and treatment.
Each of these software types requires a different set of skills and expertise, and each has its own challenges and opportunities for diversity and inclusion in software engineering.
Inherent difficulties refer to challenges or obstacles that are inherent or intrinsic to a particular task or activity. In the context of software development, inherent difficulties refer to challenges that are specific to software development processes and projects. Some inherent difficulties in software development include:
-
Complexity: Software development involves working with complex systems and processes, which can be difficult to manage and maintain.
-
Changing requirements: Requirements for software projects can change frequently, making it difficult to deliver a product that meets all of the customer's needs.
-
Integration: Software development often involves integrating multiple systems and technologies, which can be challenging and time-consuming.
-
Security: Ensuring the security of software applications is a major challenge, as new vulnerabilities and threats are constantly emerging.
-
Testing and debugging: Identifying and fixing bugs in software applications can be time-consuming and difficult, particularly for complex applications.
-
Project management: Managing software development projects requires careful planning, coordination, and communication, which can be difficult to achieve in practice.
-
Scalability: Developing software that can scale to handle large numbers of users or data volumes can be challenging, particularly when dealing with complex systems and architectures.
Planning, managing, and executing software projects effectively is crucial to mitigating the effects of these inherent difficulties. In order to address some of these challenges, and to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the software development process, software engineering best practices, such as agile development, continuous integration, and automated testing, can be utilized effectively.
Software complexity is a natural byproduct of the functional complexity that the code is attempting to enable. With multiple system interfaces and complex requirements, the complexity of software systems sometimes grows beyond control, rendering applications and portfolios overly costly to maintain and risky to enhance. The software complexity are come from:
-
Application domain: Application domain refers to the specific area of application or field in which a software system is designed to operate. It encompasses the knowledge, concepts, and terminology that are relevant to a particular application area, as well as the constraints and requirements that are specific to that domain.
-
Communication among stakeholders (clients, developers): Effective communication between domain experts and developers is crucial for the success of software projects. Domain experts have deep knowledge of the application domain, including its terminology, concepts, and requirements. Developers, on the other hand, have expertise in software development, including programming languages, software design, and testing.
-
Management of large software development projects: Management of large software development projects is a complex task that requires careful planning, effective communication, and efficient use of resources. The key strategies that can be used to manage large software development projects are develop a detailed project plan, break down the project into smaller tasks, define clear roles and responsibilities, use project management tools and monitor project risks.
Software complexity can lead to software quality problems. The reason that lead to these problems are:
-
Increased likelihood of defects: As software becomes more complex, the likelihood of defects increases. This is because there are more opportunities for errors to occur, and it becomes more difficult to ensure that all possible scenarios have been tested. As a result, complex software may be more likely to contain bugs or other defects that can impact its quality.
-
Difficulty in understanding and maintaining the code: Complex software can be difficult to understand and maintain, which can lead to quality problems. Developers may struggle to identify bugs or make changes to the code, leading to errors and defects. This can be particularly problematic when multiple developers are working on the same codebase, as inconsistencies and conflicts can arise.
-
Poor performance: Complex software can also suffer from poor performance, as it may require more processing power or memory to run effectively. This can lead to crashes or other quality problems that impact the user experience.
-
Inconsistencies in user experience: Complex software can also lead to inconsistencies in the user experience, as different parts of the software may behave differently or have different design patterns. This can lead to confusion and frustration among users, which can impact their perception of the software's quality.
Here are some of the examples of software quality problems that have occurred around the world:
-
Y2K Bug: In the late 1990s, there was concern that many computer systems would experience problems when the year 2000 arrived, due to the way dates were stored. This was known as the Y2K bug, and many organizations spent significant time and resources updating their software to prevent problems.
-
Ariane 5 Rocket Failure: In 1996, the maiden flight of the Ariane 5 rocket ended in failure due to a software error. The rocket's software was not designed to handle the faster speed of the new rocket, leading to a crash that destroyed the rocket and its payload.
-
Volkswagen Emissions Scandal: In 2015, it was discovered that Volkswagen had installed software in its diesel cars that allowed them to cheat emissions tests. This led to a scandal that affected millions of cars around the world, and caused significant damage to Volkswagen's reputation.
-
Healthcare.gov Launch Issues: In 2013, the launch of the Healthcare.gov website in the United States was marred by numerous software quality problems. The website was slow, buggy, and difficult to use, which led to significant criticism and delays in the enrollment process.
Overall, software complexity can have a significant impact on software quality. To mitigate these issues, developers should focus on simplifying the software design, reducing the number of components, and thoroughly testing the software to identify and fix defects before release. Additionally, they should prioritize effective communication and collaboration among team members, to ensure that everyone is on the same page and working towards the same goals.
Software changeability refers to the ease with which modifications can be made to a software system. In other words, it refers to the ability of software to adapt to changes and evolve over time. Changeability is an important factor in software development as it can affect the maintenance, scalability, and overall quality of the software.
The changeability of a software system is influenced by various factors, such as the design of the system, the programming language used, the tools and techniques employed, and the level of documentation and testing. A well-designed software system that is modular and loosely coupled can be more changeable as changes to one component will have minimal impact on the others. Similarly, using a programming language that supports features such as inheritance, polymorphism, and abstraction can make the software more adaptable to changes.
To improve the changeability of a software system, it is important to follow best practices such as writing clean code, using version control systems, writing automated tests, and documenting the code. By doing so, developers can make it easier to understand, modify, and maintain the software over time, which can ultimately lead to a more robust and reliable system.
Computer science and software engineering may share some overlapping commonalities, however, the principles behind each field can offer several differences. One is that computer science deals with the science behind the interaction between hardware and software systems and computational applications, whereas software engineering typically deals with the engineering principles of building, designing and testing software products.The differences of computer science and software engineering are:
-
Core educational studies: Computer science and software engineering may share some overlapping core studies, however, when studying computer science students may typically complete courses that focus on the computing, analysis, storage and application of data and data systems of computer programs and software. Computer science education program focuses on the science behind making computers work, while software engineering applies those scientific and mathematical principles to the building, designing and implementation of hardware and software programs.
-
Career paths: Generally, computer science degrees may offer candidates a broad range of job options in the informational technology industry, from computer programming for website design and working in IT support roles to working as a game developer. Conversely, a degree in software engineering can narrow a candidate's career path to specialized roles in corporations, companies and even mid-sized businesses developing and building applications and software programs.
-
Hardware and software interaction: Computer science may deal with the interaction between software programs with computer hardware. For instance, a computer scientist might determine ways to create software programs that are compatible with computer hardware. A software engineer, however, deals only with software programs, specifically creating, maintaining, testing and producing software products.
-
Programming and development: Computer science will focus on computing and calculating the best ways to program software as well as finding calculations that allow engineers and developers to build software programs that meet product requirements. Software engineers essentially use the analysis and outlines from computer scientists to aid in the full development and construction of new frameworks and software programs.
-
Software design: When approaching software design, a computer scientist may typically work with theories and algorithms for how a program works, how it may be best designed and how to apply programming languages to the application. When software engineers work with software design, they may use a computer scientist's information and analyses to design the framework to build a specific program.
-
Scientific theories: Computer science is also different from software engineering because it focuses heavily on scientific theories behind computer operations, computing and data systems as well as how software is designed. Software engineering, however, can use these theories to aid in the design and processes of building frameworks, software programs and applications. So while computer science studies and develops theories behind computer operations, software engineering applies these theories to build real-world computer applications.
-
Computer coding: Computer science and software engineering may both focus on computer coding and languages, however, software engineering may focus more heavily on learning coding to use it when developing and building software. A computer scientist may focus on coding as it relates to computer languages, and they may also use various computer coding to calculate compatibility between hardware and software applications.
In summary, computer science is the study of computing and computational systems, while software engineering is the practical application of computer science principles to software development.Both are the best in their own aspects. However, you should optional for the Software engineering if you are interested in software testing, software development and overall software life cycle or you can optional for Computer Science if you have an interest in artificial intelligence, machine learning, security, database management, etc.
Software Programming , also known as software development or coding, refers to the process of writing and maintaining the source code of software programs. This includes designing, coding, testing, and debugging software applications. A software programmer's main focus is on writing efficient and functional code that meets the requirements of the project.For software programming:
-
Programming is primarily a single person activity.
-
A computer programmer writes an entire program.
-
Programming is simply one side of software system development.
-
On an average computer, the programmer makes a salary of $78,260 a year.
-
A computer programmer is aware of the way to code and will have the technical skills required to create significant merchandise.
-
A programmer tends to work alone.
-
Computer Programmer takes a broad approach to the study of the principles and use of computers that covers each theory and application.
-
A computer programmer hired to produce the code of a computer program. It will imply that you know how to write code, can understand an algorithm and follow specification.
In essence, software programming is a subset of software engineering. While software programming is primarily concerned with the implementation of code, software engineering is focused on the entire software development process, including requirements analysis, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance. For software programming:
-
Software Engineer develops a software system part which will be combined with parts written by different software system engineers to create a system.
-
Software Engineering is basically a team activity.
-
Large software system systems should be developed like different engineering practices.
-
The software system engineers can take a salary of $93,280 a year.
-
A software engineer follows a scientific method of understanding necessities, operating with stakeholders and developing an answer that fulfills their needs.
-
A software engineer is an element of a bigger team.
-
On the opposite hand, Software Engineering could be a field mostly involved with the appliance of engineering processes to the creation, maintenance, and style of a software system for a range of various functions.
-
A software engineer is a developer who has a specific type of degree, some knowledge of engineering, and is capable of designing a system. Basically, software engineer sees a wider picture, and are capable of designing and explaining it and separating it into smaller modules.
In summary, software programming is a subset of software engineering. While software programming is concerned with the creation of software applications by writing code, software engineering focuses on the entire software development lifecycle, including the management of the process, development of best practices, and design of software systems that are efficient, scalable, and maintainable.
Quality focus in software development refers to the emphasis placed on delivering high-quality software products that meet or exceed customer expectations. It involves the integration of quality standards and practices throughout the entire software development process.
External quality focus refers to the quality of the software product that is delivered to the end-users or customers. It ensures that the software meets or exceeds the customer's expectations and provides a positive user experience. External quality focus involves the following:
-
Functional requirements: The software meets the functional requirements that the customer has specified.
-
Performance: The software performs efficiently, has good response times, and can handle large amounts of data.
-
Reliability: The software operates reliably, with minimal downtime or errors.
-
Usability: The software is easy to use and understand, with a good user interface.
-
Security: The software is secure and protects sensitive data from unauthorized access or theft.
Internal quality focus refers to the quality of the software development process itself. It ensures that the software development process is efficient, effective, and produces high-quality software products. Internal quality focus involves the following:
-
Code quality: The code is well-structured, follows coding standards, and is easy to read and maintain.
-
Testing: The software is thoroughly tested, with automated testing and manual testing, to ensure that it meets the functional and non-functional requirements.
-
Documentation: The software is well-documented, with clear and concise documentation for developers, testers, and end-users.
-
Continuous integration and delivery: The software development process includes continuous integration and delivery, which ensures that code changes are frequently and automatically integrated and tested.
There are various factors that contribute to software quality, including functionality, reliability, usability, efficiency, maintainability, and portability. Here are a few examples of software quality:
-
Functionality: Software that performs its intended functions correctly and completely. For example, a word processing software that allows users to create, edit, and format documents without errors.
-
Reliability: Software is more reliable if it has fewer failures. Since software engineers do not deliberately plan for their software to fail, reliability depends on the number and types of mistakes they make.
-
Usability: The higher the usability of software, the easier it is for users to work with it. There are several aspects of usability, including learnability for novices, efficiency of use for experts and handling of errors.
-
Efficiency: Software should not make wasteful use of system resources such as memory and processor cycles. Efficiency therefore includes responsiveness, processing time, memory utilisation, etc.
-
Maintainability: Software should be written in such a way so that it can evolve to meet the changing needs of customers. This is a critical attribute because software change is an inevitable requirement of a changing business environment.
-
Portability: Software that can run on different hardware platforms and operating systems. For example, a web application that can run on different web browsers and operating systems.
The priority of software quality varies depending on the software development project, the intended users, and the organization's goals. However, in general, software quality should always be a top priority, as it has a significant impact on the success of a software product and the overall reputation of the organization.
Here are some factors that can influence the priority of software quality:
-
Customer requirements: The quality of the software should meet or exceed the customer's requirements and expectations. If the customer requires a high-quality software product, then the priority of software quality should be high.
-
Time-to-market: If a software product needs to be released quickly to meet market demand or competition, then the priority of software quality may be lower. However, this should not compromise the software's functional or performance requirements.
-
Cost: The priority of software quality may be affected by the project's budget. If there are limited resources, the focus may be on meeting the minimum requirements while ensuring the software is reliable and maintainable.
-
Criticality of the software: If the software product is critical to the organization's operations or safety, then the priority of software quality should be high. For example, software used in healthcare, aviation, or finance must meet strict quality standards to ensure safety and reliability.
-
Technical complexity: If the software product is complex, with many components or integration points, then the priority of software quality should be high. Complex software requires more testing and verification to ensure that it operates correctly.
In summary, software quality should always be a priority, but the level of priority may vary depending on the specific project's requirements, time-to-market, budget, criticality, and technical complexity. The ultimate goal should always be to deliver a high-quality software product that meets or exceeds customer expectations, is reliable, scalable, and maintainable over the long term.
Software standards are a set of guidelines or criteria that describe best practices for the development, design, and maintenance of software. These standards are typically developed by professional organizations or regulatory bodies to ensure consistency and quality across software products.
There are various types of software standards, including coding standards, testing standards, and documentation standards. Coding standards define the rules and conventions for writing source code, while testing standards specify the procedures and techniques for testing software. Documentation standards dictate the format and content of documents produced during the software development process, such as design documents, user manuals, and technical specifications.
Software documentation is an important part of the software development process. It involves creating and maintaining various types of documents that describe the software's design, functionality, and operation. Documentation can include user manuals, technical specifications, design documents, code comments, and help files.
The purpose of software documentation is to provide a clear and comprehensive understanding of the software to users, developers, and other stakeholders. Good documentation can help to reduce errors, improve maintainability, and facilitate collaboration among team members. It can also help to ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations.
Overall, software standards and documentation are essential components of the software development process. By following established standards and producing high-quality documentation, software developers can improve the quality, reliability, and usability of their products.
Please create an Issue for any e
- If follow the prescribed software engineering methods, it will save the precious time by decreasing it.
- This can be seen in industries such as finance and manufacturing, where software is used to automate processes and reduce the likelihood of human error.
- The software will be reliable if software engineering, testing, and maintenance are given.
- By applying engineering principles and rigorous testing methodologies, software engineers can identify and correct potential issues before they impact end-users.
- Software engineering fosters collaboration among developers, designers, and stakeholders, which helps ensure that software systems are developed with the end user in mind. This collaboration also helps improve communication, reduce errors, and ensure that software meets the needs of all stakeholders.
<li>Ensuring security and privacy</li>
<ul>
<li>Software engineers can design systems that are resistant to cyberattacks and ensure that user data is
protected.</li>
</ul>
</ol>
<p> Overall, software engineering is a vital discipline that plays an important role in many areas of modern
society.
Its benefits include improved quality and reliability of software systems, increased efficiency and automation,
improved security and privacy, and the ability to drive innovation and advance technology.</p>