English | 简体中文
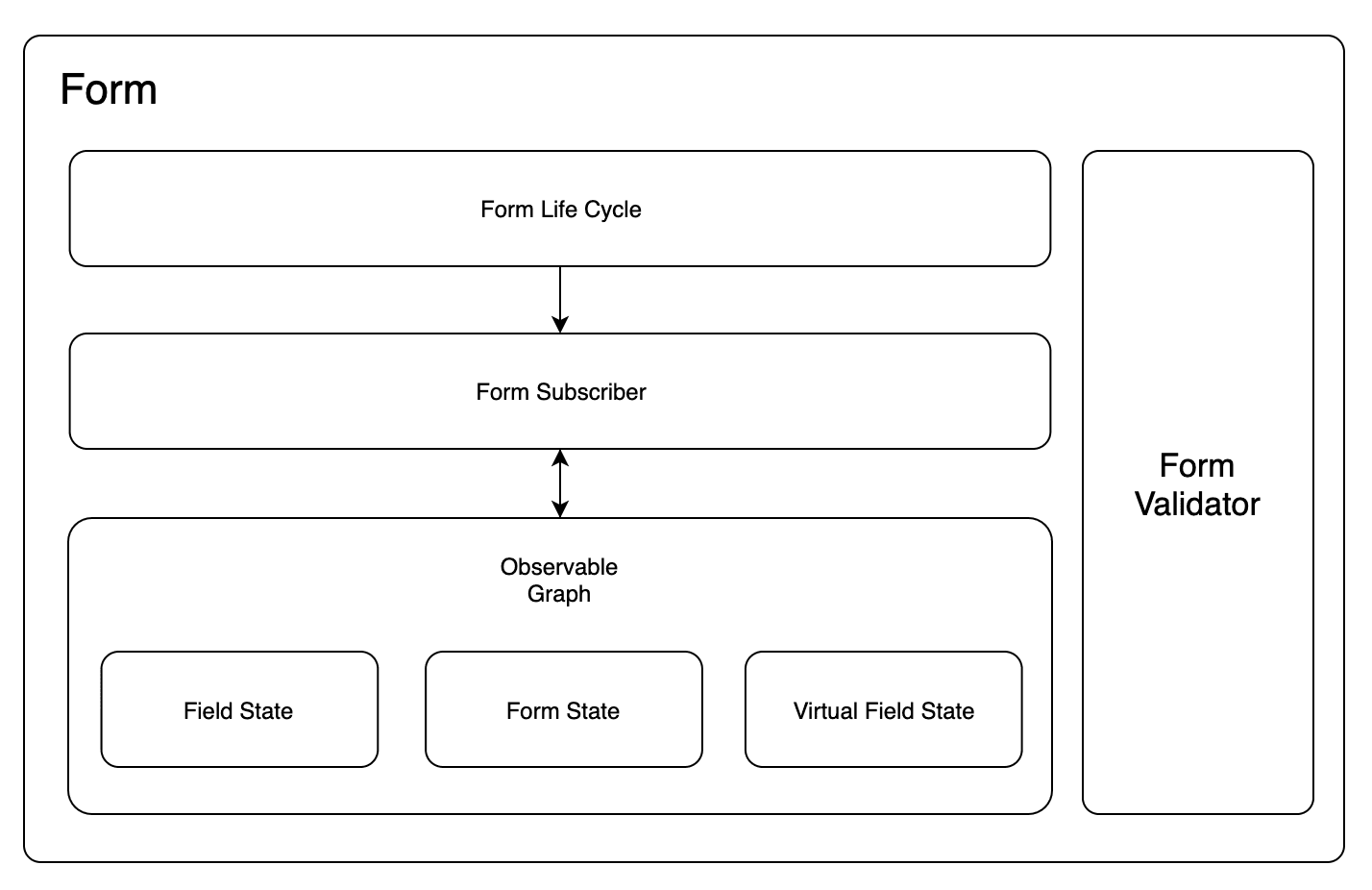
The form state core management package does not rely on any third-party UI frameworks. This package will provide the following features:
- Manage Form status
- Manage Field status
- Manage the Validator status
- Manage dependencies between Form, Field, and Validator
npm install --save @formily/core- Backdrop
- Design Concept
- Core highlights
- Architecture diagram
- Terminology explanation
- API
- Classes
- Enums
- Interfaces
There are two main scenarios in the middle and back-end field, one is data entry, one is data query + data presentation, whether it is data entry or data query, it is realized by means of form, from the perspective of implementation complexity, the complexity of them is similar, because the data rendering level will inevitably have extremely complex renderings (such as Tree Table, etc.), but the data rendering is easier to reuse and abstract, only the Form requirements will involve a lot of interactive logic. So, as long as we solve the Form problem fundamentally, for the mid- and back-stage scenes, most of the mid- and back-stage scene problems are solved.
Formily is born for this purpose.
Anything comes from Observable Graph.
-
Time travel, with the help of the Observable Graph, can record the full state at any time, can also roll back the state to any time, such abilities will maximize the performance in heavy transaction applications and local debugging scenarios.
-
Efficient update, accurate rendering, no full tree rendering required
-
Built-in immer.js, intelligent degradation, no need to care about browser compatibility
-
More complete life cycle hook
-
More complete verification engine
-
- ValidateFirst verification
- Warning Verification (no blocking submission verification)
- Verification message template engine (a complex verification message solution that does not affect international copy storage)
- The verification rule can be extended, and the regular verification library can be extended.
-
More flexible path parsing, matching, evaluation, value engine
-
- Batch matching data path capability
- Deconstruct evaluation, deconstruct value ability
-
Provides state management capabilities beyond the basic form state model.
FormPath/FormPathPattern Is an abstract data path form, FormPath is a path class, and FormPathPattern is a path form that can be parsed by FormPath. Cool-path Path parsing matching, ability to evaluate values
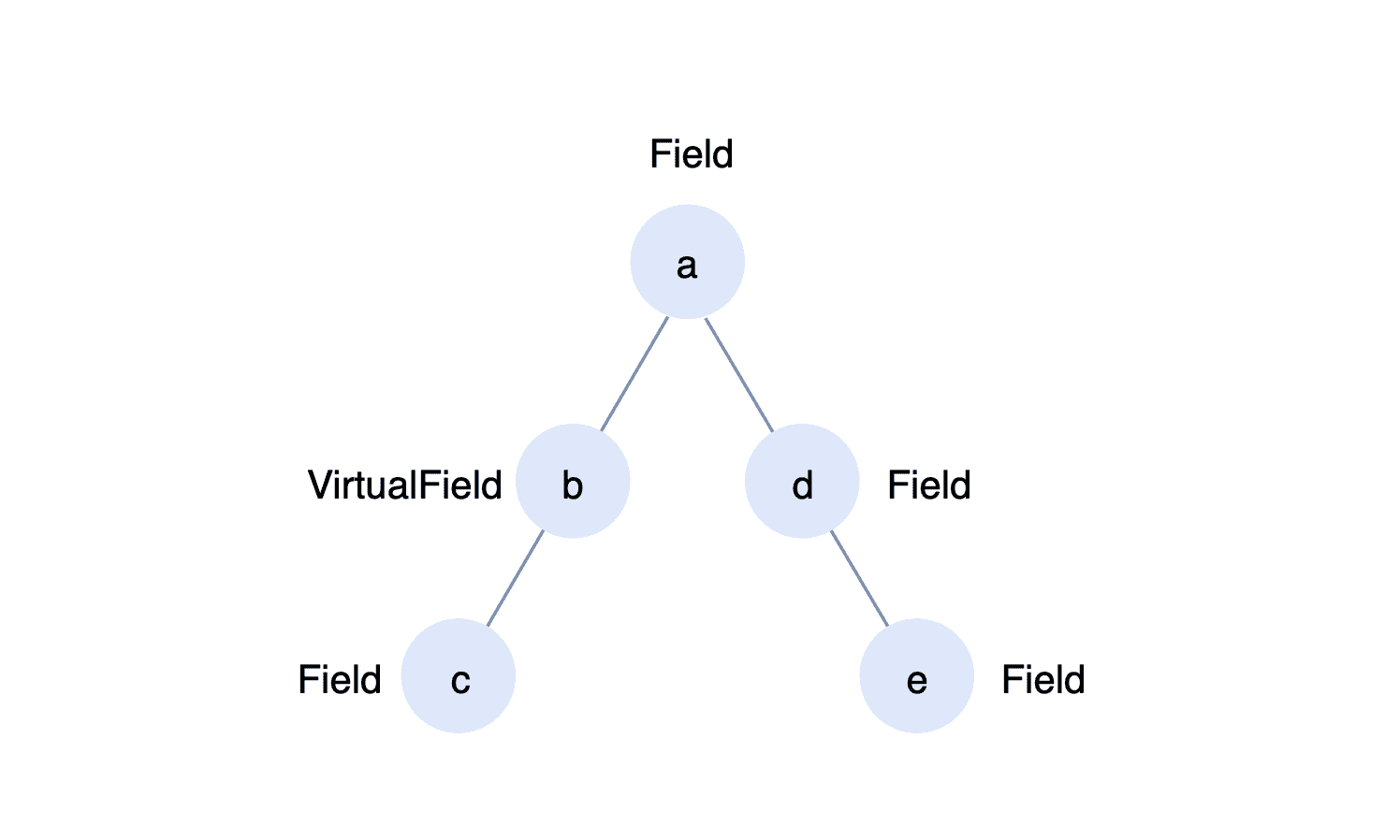
The virtual field Is a special Field data structure. The difference between the Field and the Field is that it does not manage values. That is to say, it has no relevance to the value of the Form. Usually we use it, more importantly, it acts as a proxy for the status of a UI container. For example, the layout component FormBlock in Formily exists as an independent node in the whole Form Graph, however, this node type is a VirtualField, but when the final data is submitted, the FormBlock does not pollute the data structure of the submitted data.
Observable Graph Form is a unique Observer Tree. With the help of the observer tree, many forms-related internal linkage logic can be implemented.
Data Path Is the name attribute of Field/VirtualField, which exists as the data path.
Node Path Is the path attribute of Field/VirtualField, which exists as the node path.
For the data path and node path, we can look at the following figure:
If there exists such a tree, then:
- The name attribute of field c is a.c, and the path attribute is a.b.c.
- The name attribute of field B is a.b, and the path attribute is a.b.
- The name attribute of field d is a.d, and the path attribute is a.d.
- The name attribute of field e is a.d.e, and the path attribute is a.d.e.
After this explanation, we roughly understand that as long as VirtualField exists in a node path, its data path will skip VirtualField. However, for VirtualField itself, its name attribute contains its own node identification, which is why the name attribute of field B is a.b.
Create a Form instance
Signature
createForm(options?: IFormCreatorOptions): IForm
Usage
import { createForm } from '@formily/core'
const form = createForm({
values:{},
initialValues:{},
onChange:(values)=>{
console.log(values)
}
})
const aa = form.registerField({
path:"aa"
})
aa.setState(state=>{
state.value = 123
})
console.log(form.getFormState(state=>state.values)) //{aa:123}
Register a regular verification rule set
Signature
registerValidationFormats(formats:{
[formatName in string]: RegExp;
}) : void
Usage
import { createForm,registerValidationFormats } from '@formily/core'
registerValidationFormats({
number: /^[+-]?\d+(\.\d+)?$/
})
const form = createForm({
values:{},
initialValues:{},
onChange:(values)=>{
console.log(values)
}
})
const aa = form.registerField({
path:"aa",
rules:[{
format:"number",
message:'This field is not a number.'
}]
})
aa.setState(state=>{
state.value = 'hello world'
})
form.validate()
console.log(form.getFormState(state=>state.errors))
/**
[{
path: 'aa',
messages: [ 'This field is not a number.' ]
}]
**/
The difference between registering a verification rule set and registering formats is that it can register complex verification rules, but the formats are just regular expressions.
Signature
registerValidationRules(
rules:{
[ruleName:string]:(value:any,rule:ValidateDescription)=>boolean
}
) : void
Usage
import { createForm,registerValidationRules } from '@formily/core'
registerValidationRules({
custom: value => {
return value === '123' ? 'This field can not be 123' : ''
}
})
const form = createForm({
values: {},
initialValues: {},
onChange: values => {
console.log(values)
}
})
const aa = form.registerField({
path: 'aa',
rules: [
{
custom: true
}
]
})
aa.setState(state => {
state.value = '123'
})
form.validate()
console.log(form.getFormState(state =>state.errors))
/**
[{
path: 'aa',
messages: ['This field can not be 123']
}]
**/
Register a verification message template engine
Signature
registerValidationMTEngine(callback:(message,context)=>any) : void
Usage
import { createForm,registerValidationMTEngine } from '@formily/core'
registerValidationMTEngine((message,context)=>{
return message.replace(/\{\{\s*(\w+)\s*\}\}/g, (_, $0) => {
return FormPath.getIn(context, $0)
})
})
const form = createForm({
values: {},
initialValues: {},
onChange: values => {
console.log(values)
}
})
const aa = form.registerField({
path: 'aa',
rules: [
{
validator(value){
return value === 123 : 'This field can not be 123 {{scope.outerVariable}}'
},
scope:{
outerVariable:'addonAfter'
}
}
]
})
aa.setState(state => {
state.value = '123'
})
form.validate()
console.log(form.getFormState(state =>state.errors))
/**
[{
path: 'aa',
messages: ['This field can not be 123 addonAfter']
}]
**/
Set the international language type
Signature
setValidationLanguage(lang: string): void
Usage
import { setValidationLanguage } from '@formily/core'
setValidationLanguage('en-US')
Set a language pack
Signature
interface ILocaleMessages {
[key: string]: string | ILocaleMessages;
}
interface ILocales {
[lang: string]: ILocaleMessages;
}
setValidationLocale(locale: ILocales) => void
Usage
import { setValidationLocale } from '@formily/core'
setValidationLocale({
'en-US':{
required:"This field is required."
}
})
The form path engine is responsible for path analysis, matching, evaluation, value, deconstruction evaluation, and deconstruction value.
For more information, see: https://github.com/janrywang/cool-path
Create a life cycle listener
Signature
type FormLifeCycleHandler<T> = (payload: T, context: any) => void
new FormLifeCycle(handler: FormLifeCycleHandler<Payload>)
new FormLifeCycle(...type: LifeCycleTypes, handler: FormLifeCycleHandler<Payload>...)
new FormLifeCycle(handlerMap: { [key: LifeCycleTypes]: FormLifeCycleHandler<Payload> })
Usage
import { createForm,FormLifeCycle,LifeCycleTypes } from '@formily/core'
const form = createForm({
lifecycles:[
new FormLifeCycle(({type:LifeCycleTypes,payload:IForm | IField | IVirtualField })=>{
// God mode, full monitoring
}),
new FormLifeCycle(
LifeCycleTypes.ON_FORM_MOUNT,
(payload:IForm | IField | IVirtualField)=>{
// Accurate monitoring
}),
new FormLifeCycle({
[LifeCycleTypes.ON_FORM_MOUNT]:(payload:IForm | IField | IVirtualField)=>{
// Object form accurate listener
}
}),
]
})enum LifeCycleTypes { // Form pre-initialization trigger
/**
* Form LifeCycle
**/ ON_FORM_WILL_INIT = 'onFormWillInit',
// Form initialization trigger
ON_FORM_INIT = 'onFormInit',
// Triggered when the form changes
ON_FORM_CHANGE = 'onFormChange',
// Triggered when the form is mounted
ON_FORM_MOUNT = 'onFormMount',
// Triggered when the form is unloaded
ON_FORM_UNMOUNT = 'onFormUnmount',
// Triggered when the form is submitted
ON_FORM_SUBMIT = 'onFormSubmit',
// Triggered when the form is reset
ON_FORM_RESET = 'onFormReset',
// Triggered when the form submission starts
ON_FORM_SUBMIT_START = 'onFormSubmitStart',
// Triggered when the form submission ends
ON_FORM_SUBMIT_END = 'onFormSubmitEnd',
// Triggered when the form submission within validate
ON_FORM_SUBMIT_VALIDATE_START = 'onFormSubmitValidateStart',
// Triggered when the form submission ends due to validate successs
ON_FORM_SUBMIT_VALIDATE_SUCCESS = 'onFormSubmitValidateSuccess',
// Triggered when the form submission ends due to validate failed
ON_FORM_SUBMIT_VALIDATE_FAILED = 'onFormSubmitValidateFailed',
// Triggered when the onSubmit success
ON_FORM_ON_SUBMIT_SUCCESS = 'onFormOnSubmitSuccess',
// Triggered when the onSubmit failed
ON_FORM_ON_SUBMIT_FAILED = 'onFormOnSubmitFailed',
// Triggered when the form value changes
ON_FORM_VALUES_CHANGE = 'onFormValuesChange',
// Trigger when the form initial value changes
ON_FORM_INITIAL_VALUES_CHANGE = 'onFormInitialValuesChange',
// Triggered when form validation begins
ON_FORM_VALIDATE_START = 'onFormValidateStart',
// Triggered when the form validation ends
ON_FORM_VALIDATE_END = 'onFormValidateEnd',
// Triggered when the form event is triggered, used to monitor only manual operations
ON_FORM_INPUT_CHANGE = 'onFormInputChange', // Triggered when the form observer tree changes
/**
* FormGraph LifeCycle
**/ ON_FORM_GRAPH_CHANGE = 'onFormGraphChange', // Triggered when pre-initialized
/**
* Field LifeCycle
**/ ON_FIELD_WILL_INIT = 'onFieldWillInit',
// Triggered when the field is initialized
ON_FIELD_INIT = 'onFieldInit',
// Triggered when the field changes
ON_FIELD_CHANGE = 'onFieldChange',
// Triggered when the field event is triggered, used to monitor only manual operations
ON_FIELD_INPUT_CHANGE = 'onFieldInputChange',
// Triggered when the field value changes
ON_FIELD_VALUE_CHANGE = 'onFieldValueChange',
// Trigger when the initial value of the field changes
ON_FIELD_INITIAL_VALUE_CHANGE = 'onFieldInitialValueChange',
// Triggered when the field is mounted
ON_FIELD_MOUNT = 'onFieldMount',
// Trigger when the field is unloaded
ON_FIELD_UNMOUNT = 'onFieldUnmount'
}CreateForm parameter object protocol
interface IFormCreatorOptions {
// Form initial value
initialValues?: {} // Form value
values?: {} // LifeCycle listener, here mainly introduced to the instantiated object of FormLifeCycle
lifecycles?: FormLifeCycle[] // Is it editable, overall control in the Form dimension
editable?: boolean | ((name: string) => boolean) // Whether to use the dirty check, the default will go immer accurate update
useDirty?: boolean // Whether to go pessimistic check, stop the subsequent check when the first check fails
validateFirst?: boolean // Form change event callback
onChange?: (values: IFormState['values']) => void // Form submission event callback
onSubmit?: (values: IFormState['values']) => any | Promise<any> // Form reset event callback
onReset?: () => void // Form verification failure event callback
onValidateFailed?: (validated: IFormValidateResult) => void
}Form instance object API created by using createForm
interface IForm {
/*
* Form submission, if the callback parameter returns Promise,
* Then the entire submission process will hold and load is true.
* Wait for Promise resolve to trigger the form onFormSubmitEnd event while loading is false
*/
submit(
onSubmit?: (values: IFormState['values']) => any | Promise<any>
): Promise<{
Validated: IFormValidateResult
Payload: any //onSubmit callback function return value
}>
/*
* Clear the error message, you can pass the FormPathPattern to batch or precise control of the field to be cleared.
* For example, clearErrors("*(aa,bb,cc)")
*/
clearErrors: (pattern?: FormPathPattern) => void
/*
* Get status changes, mainly used to determine which states in the current life cycle have changed in the form lifecycle hook.
* For example, hasChanged(state,'value.aa')
*/
hasChanged(
target: IFormState | IFieldState | IVirtualFieldState,
path: FormPathPattern
): boolean
/*
* Reset form
*/
reset(options?: {
// Forced to empty
forceClear?: boolean // Forced check
validate?: boolean // Reset range for batch or precise control of the field to be reset
selector?: FormPathPattern
clearInitialValue?: boolean //Clear initialValue
}): Promise<void | IFormValidateResult>
/*
* Validation form, throw IFormValidateResult when validation fails
*/
validate(
path?: FormPathPattern,
options?: {
// Is it pessimistic check, if the current field encounters the first verification error, stop the subsequent verification process
first?: boolean
}
): Promise<IFormValidateResult>
/*
* Set the form status
*/
setFormState( // Operation callback
callback?: (state: IFormState) => any, // No trigger the event
silent?: boolean
): void
/*
* Get form status
*/
getFormState( //transformer
callback?: (state: IFormState) => any
): any
/*
* Set the field status
*/
setFieldState( // Field path
path: FormPathPattern, // Operation callback
callback?: (state: IFieldState) => void, // No trigger the event
silent?: boolean
): void
/*
* Get the field status
*/
getFieldState( // Field path
path: FormPathPattern, // Transformer
callback?: (state: IFieldState) => any
): any
/*
* Registration field
*/
registerField(props: {
// Node path
path?: FormPathPattern // Data path
name?: string // Field value
value?: any // Field multi-value
values?: any[] // Field initial value
initialValue?: any // Field extension properties
visible?: boolean //Field initial visible status(Whether the data is visible)
display?: boolean //Field initial display status(Whether the style is visible)
props?: any // Field check rule
rules?: ValidatePatternRules[] // Field is required
required?: boolean // Is the field editable?
editable?: boolean // Whether the field is dirty check
useDirty?: boolean // Field state calculation container, mainly used to extend the core linkage rules
computeState?: (draft: IFieldState, prevState: IFieldState) => void
}): IField
/*
* Register virtual fields
*/
registerVirtualField(props: {
// Node path
path?: FormPathPattern // Data path
name?: string // Field extension properties
visible?: boolean //Field initial visible status(Whether the data and style is visible)
display?: boolean //Field initial display status(Whether the style is visible)
props?: any // Whether the field is dirty check
useDirty?: boolean // Field state calculation container, mainly used to extend the core linkage rules
computeState?: (draft: IFieldState, prevState: IFieldState) => void
}): IVirtualField
/*
* Create a field data operator, which will explain the returned API in detail later.
*/
createMutators(field: IField | FormPathPattern): IMutators
/*
* Get the form observer tree
*/
getFormGraph(): IFormGraph
/*
* Set the form observer tree
*/
setFormGraph(graph: IFormGraph): void
/*
* Listen to the form life cycle
*/
subscribe(
callback?: ({ type, payload }: { type: string; payload: any }) => void
): number
/*
* Cancel the listening form life cycle
*/
unsubscribe(id: number): void
/*
* Trigger form custom life cycle
*/
notify: <T>(type: string, payload?: T) => void
/*
* Set the field value
*/
setFieldValue(path?: FormPathPattern, value?: any): void
/*
* Get the field value
*/
getFieldValue(path?: FormPathPattern): any
/*
* Set the initial value of the field
*/
setFieldInitialValue(path?: FormPathPattern, value?: any): void
/*
* Get the initial value of the field
*/
getFieldInitialValue(path?: FormPathPattern): any
}The instance API created by crewikiutators is mainly used to operate field data.
interface IMutators {
// Changing the field value and multi parameter condition will store all parameters in values
change(...values: any[]): any
// Get focus, trigger active state change
focus(): void
// Lose focus, trigger active / visited status change
blur(): void
// Trigger current field verifier
validate(): Promise<IFormValidateResult>
// Whether the value of the current field exists in the values property of form
exist(index?: number | string): Boolean
/**Array operation method**/
// Append data
push(value?: any): any[]
// Pop up tail data
pop(): any[]
// Insert data
insert(index: number, value: any): any[]
// Delete data
remove(index: number | string): any
// Head insertion
unshift(value: any): any[]
// Head ejection
shift(): any[]
// Move element
move($from: number, $to: number): any[]
// Move down
moveDown(index: number): any[]
// Move up
moveUp(index: number): any[]
}Here we mainly list the intermediate type signatures related to verification.
type CustomValidator = (
value: any,
description?: ValidateDescription
) => ValidateResponse
type SyncValidateResponse =
| null
| string
| boolean
| {
type?: 'error' | 'warning'
message: string
}
type AsyncValidateResponse = Promise<SyncValidateResponse>
type ValidateResponse = SyncValidateResponse | AsyncValidateResponse
interface IFormValidateResult {
errors: Array<{
path: string
messages: string[]
}>
warnings: Array<{
path: string
messages: string[]
}>
}
type InternalFormats =
| 'url'
| 'email'
| 'ipv6'
| 'ipv4'
| 'idcard'
| 'taodomain'
| 'qq'
| 'phone'
| 'money'
| 'zh'
| 'date'
| 'zip'
| string
interface ValidateDescription {
// Regular rule type
format?: InternalFormats
// Custom validator
validator?: CustomValidator
// Is it required?
required?: boolean
// Customize with regularity
pattern?: RegExp | string
// Maximum length rule
max?: number
// Maximum numerical rule
maximum?: number
// Exclusive maximum numerical rule
exclusiveMaximum?: number
// Exclusive minimum numerical rules
exclusiveMinimum?: number
// Minimum value rule
minimum?: number
// Minimum length rule
min?: number
// Length rule
len?: number
// Whether to check the white space
whitespace?: boolean
// Enumeration check rules
enum?: any[]
// Custom error copy
message?: string
// Custom validation rules
[key: string]: any
}Form the core state
interface IFormState<FormProps = any> {
/**Read-only attribute**/
// Is it in the original state, pristine is true only when values === initialValues
pristine: boolean // Is it legal, as long as the error length is greater than 0, the valid is false
valid: boolean // Is it illegal, as long as the error length is greater than 0, the valid is true
invalid: boolean // Is it in the check state, it will only be set when calling the validate API
validating: boolean // Is it in the commit state, it will only be set when the submit API is called
submitting: boolean //Error message list
errors: string[] //Alarm message list
warnings: string[] /** writable property**/ // Is it in the loaded state, writable state, as long as validating is true, the state will also be true, the same as false
loading: boolean // Is it in the initial state?
initialized: boolean // Is it editable?
editable: boolean | ((name: string) => boolean) // form value
values: {} // form initial value
initialValues: {} // form mount, the life cycle hook mentioned earlier, must be triggered by setting the state, the default will not trigger
mounted: boolean // Form unmount, the life cycle hook mentioned earlier, must be triggered by setting the state, the default will not trigger
unmounted: boolean // Form extension properties
props: FormProps
}CORE Field status
interface IFieldState<FieldProps = any> {
/**Read-only attribute**/
// State name, FieldState
displayName?: string // Data path
name: string // Node path
path: string // Has been initialized
initialized: boolean // Is it in the original state, the state is true only when value===initialValues
pristine: boolean // Is it in a legal state, as long as the error length is greater than 0, the valid is false
valid: boolean // Is it illegal, as long as the error length is greater than 0, the valid is true
invalid: boolean // Is it in check state?
validating: boolean // Is it modified, if the value changes, the property is true, and will be true throughout the life of the field
modified: boolean // Is it touched?
touched: boolean // Is it activated, when the field triggers the onFocus event, it will be triggered to true, when onBlur is triggered, it is false
active: boolean // Have you ever visited, when the field triggers the onBlur event, it will be triggered to true
visited: boolean /** writable property**/ // Is it visible, note: if the state is false, then the value of the field will not be submitted, and the UI will not display
visible: boolean // Whether to show, note: if the state is false, then the value of the field will be submitted, the UI will not display, similar to the form hidden field
display: boolean // Is it editable?
editable: boolean // Is it in the loading state, note: if the field is in asynchronous verification, loading is true
loading: boolean // Field multi-parameter value, such as when the field onChange trigger, the event callback passed multi-parameter data, then the value of all parameters will be stored here
values: any[] // Field error message
errors: string[] // Field alert message
warnings: string[] // Field value, is equal to values[0]
value: any // Initial value
initialValue: any // Check the rules, the specific type description refers to the following documents
rules: ValidatePatternRules[] // Is it required?
required: boolean // Whether to mount
mounted: boolean // Whether to uninstall
unmounted: boolean // field extension properties
props: FieldProps
}Virtual Field core status
interface IVirtualFieldState<FieldProps = any> {
/**Read-only status**/
// State name, VirtualFieldState
displayName: string // Field data path
name: string // Field node path
path: string // Has been initialized
initialized: boolean /** writable status**/ // Is it visible, note: if the state is false, the UI will not be displayed, the data will not be submitted (because it is a VirtualField)
visible: boolean // Whether to show, note: if the state is false, the UI will not display, the data will not be submitted (because it is VirtualField)
display: boolean // Is it mounted?
mounted: boolean // Has been uninstalled
unmounted: boolean // field extension properties
props: FieldProps
}The instance API created by using registerField/registerVirtualField
interface IField/IVirtualField {
// Batch update container
batch: (callback?: () => void) => void
// Get the status
getState: (callback?: (state: IFieldState) => any) => any
// Set the status
setState: (
callback?: (state: IFieldState | Draft<IFieldState>) => void,
silent?: boolean
) => void
// Get the source status
getSourceState: (callback?: (state: IFieldState) => any) => any
// Set the source state
setSourceState: (callback?: (state: IFieldState) => void) => void
// Get status changes
hasChanged: (key?: string) => boolean
// Get the state dirty
isDirty: (key?: string) => boolean
// Get state dirty information
getDirtyInfo: () => StateDirtyMap<IFieldState>
}