Computer vision involves analyzing patterns in visual images and reconstructing the real-world objects that produced them. The process is often broken up into two phases: feature detection and pattern recognition. Feature detection involves selecting important features of the image; pattern recognition involves discovering patterns in the features. We will investigate a particularly clean pattern recognition problem involving points and line segments. This kind of pattern recognition arises in many other applications such as statistical data analysis.
The problem.
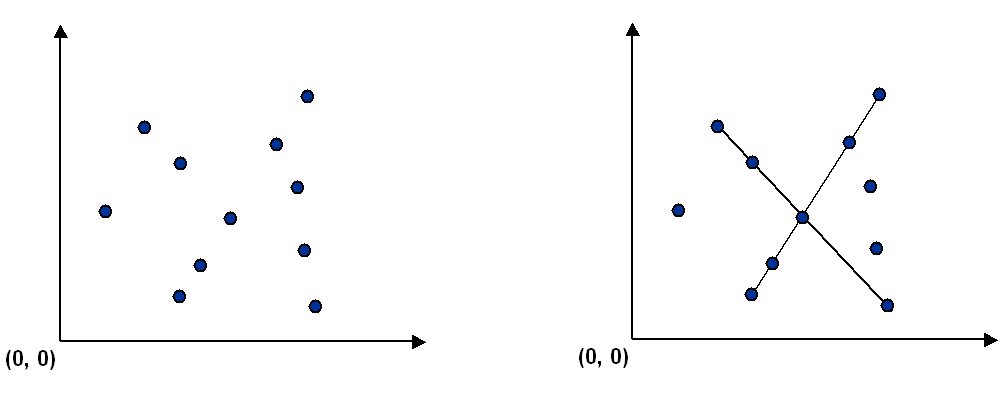
Given a set of n distinct points in the plane, find every (maximal) line segment that connects a subset of 4 or more of
the points.
Brute force method Examines 4 points at a time and checks whether they all lie on the same line segment, returning all such line segments. To check whether the 4 points p, q, r, and s are collinear, checks whether the three slopes between p and q, between p and r, and between p and s are all equal.
Fast method
Given a point p, the class determines whether p participates in a set of 4 or more collinear points. In each iteration
of a given array of points it considers "p" as the origin. First, it sorts the points by nature order and then according
to the slopes they make with "p". For each other points, determines the slope it makes with "p". Checks if any 3 (or
more) adjacent points in the sorted order have equal slopes with respect to "p". If so, these points, together with p,
are collinear and will be added to segments array.
Applying this method for each of the n points in turn yields an efficient algorithm to the problem. The algorithm solves the problem because points that have equal slopes with respect to p are collinear, and sorting brings such points together. The algorithm is fast because the bottleneck operation is sorting